| IEA EBC Annex 60 |

|
Package with base classes for Annex60.Fluid.MixingVolumes
This package contains base classes that are used to construct the models in Annex60.Fluid.MixingVolumes.
Extends from Modelica.Icons.BasesPackage (Icon for packages containing base classes).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Partial mixing volume with inlet and outlet ports (flow reversal is allowed) |
 Annex60.Fluid.MixingVolumes.BaseClasses.PartialMixingVolume
Annex60.Fluid.MixingVolumes.BaseClasses.PartialMixingVolume
Partial mixing volume with inlet and outlet ports (flow reversal is allowed)
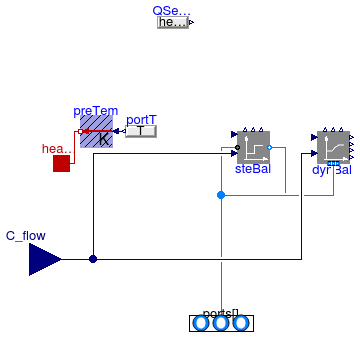
This is a partial model of an instantaneously mixed volume. It is used as the base class for all fluid volumes of the package Annex60.Fluid.MixingVolumes.
Set the constant sensibleOnly=true if the model that extends
or instantiates this model sets mWat_flow = 0.
Set the constant simplify_mWat_flow = true to simplify the equation
port_a.m_flow + port_b.m_flow = - mWat_flow;
to
port_a.m_flow + port_b.m_flow = 0;
This causes an error in the mass balance of about 0.5%, but generally leads to simpler equations because the pressure drop equations are then decoupled from the mass exchange in this component.
To increase the numerical robustness of the model, the constant
prescribedHeatFlowRate can be set by the user.
This constant only has an effect if the model has exactly two fluid ports connected,
and if it is used as a steady-state model.
Use the following settings:
prescribedHeatFlowRate=true if the only means of heat transfer
at the heatPort is a prescribed heat flow rate that
is not a function of the temperature difference
between the medium and an ambient temperature. Examples include an ideal electrical heater,
a pump that rejects heat into the fluid stream, or a chiller that removes heat based on a performance curve.
If the heatPort is not connected, then set prescribedHeatFlowRate=true as
in this case, heatPort.Q_flow=0.
prescribedHeatFlowRate=false if there is heat flow at the heatPort
computed as K * (T-heatPort.T), for some temperature T and some conductance K,
which may itself be a function of temperature or mass flow rate.prescribedHeatFlowRate=false.
Set the parameter use_C_flow = true to enable an input connector
for the trace substance flow rate.
If the model is (i) operated in steady-state,
(ii) has two fluid ports connected, and
(iii) prescribedHeatFlowRate=true or allowFlowReversal=false,
then the model uses
Annex60.Fluid.Interfaces.StaticTwoPortConservationEquation
in order to use
the same energy and mass balance implementation as is used as in
steady-state component models.
In this situation, the functions inStream are used for the two
flow directions rather than the function
actualStream, which is less efficient.
However, the use of inStream has the disadvantage
that hOut has to be computed, in
Annex60.Fluid.Interfaces.StaticTwoPortConservationEquation,
using
if allowFlowReversal then
hOut = Annex60.Utilities.Math.Functions.regStep(y1=port_b.h_outflow,
y2=port_a.h_outflow,
x=port_a.m_flow,
x_small=m_flow_small/1E3);
else
hOut = port_b.h_outflow;
end if;
Hence, for allowFlowReversal=true, if hOut
were to be used to compute the temperature that
drives heat transfer such as by conduction,
then the heat transfer would depend on upstream and the downstream
temperatures for small mass flow rates.
This can give wrong results. Consider for example a mass flow rate that is positive
but very close to zero. Suppose the upstream temperature is 20ˆC,
the downstream temperature is 10ˆC, and the heat port is
connected through a heat conductor to a boundary condition of 20ˆC.
Then, hOut = (port_b.h_outflow + port_a.h_outflow)/2 and hence
the temperature heatPort.T
is 15ˆC. Therefore, heat is added to the component.
As the mass flow rate is by assumption very small, the fluid that leaves the component
will have a very high temperature, violating the 2nd law.
To avoid this situation, if
prescribedHeatFlowRate=false, then the model
Annex60.Fluid.Interfaces.ConservationEquation
is used instead of
Annex60.Fluid.Interfaces.StaticTwoPortConservationEquation.
For simple models that uses this model, see Annex60.Fluid.MixingVolumes.
Extends from Annex60.Fluid.Interfaces.LumpedVolumeDeclarations (Declarations for lumped volumes).
| Type | Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| replaceable package Medium | PartialMedium | Medium in the component | |
| Volume | V | Volume [m3] | |
| Nominal condition | |||
| MassFlowRate | m_flow_nominal | Nominal mass flow rate [kg/s] | |
| Dynamics | |||
| Equations | |||
| Dynamics | energyDynamics | Modelica.Fluid.Types.Dynamic... | Type of energy balance: dynamic (3 initialization options) or steady state |
| Dynamics | massDynamics | energyDynamics | Type of mass balance: dynamic (3 initialization options) or steady state |
| Real | mSenFac | 1 | Factor for scaling the sensible thermal mass of the volume |
| Initialization | |||
| AbsolutePressure | p_start | Medium.p_default | Start value of pressure [Pa] |
| Temperature | T_start | Medium.T_default | Start value of temperature [K] |
| MassFraction | X_start[Medium.nX] | Medium.X_default | Start value of mass fractions m_i/m [kg/kg] |
| ExtraProperty | C_start[Medium.nC] | fill(0, Medium.nC) | Start value of trace substances |
| ExtraProperty | C_nominal[Medium.nC] | fill(1E-2, Medium.nC) | Nominal value of trace substances. (Set to typical order of magnitude.) |
| Advanced | |||
| Boolean | use_C_flow | false | Set to true to enable input connector for trace substance |
| MassFlowRate | m_flow_small | 1E-4*abs(m_flow_nominal) | Small mass flow rate for regularization of zero flow [kg/s] |
| Assumptions | |||
| Boolean | allowFlowReversal | true | = false to simplify equations, assuming, but not enforcing, no flow reversal. Used only if model has two ports. |
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VesselFluidPorts_b | ports[nPorts] | Fluid inlets and outlets |
| HeatPort_a | heatPort | Heat port for sensible heat input |
| output RealOutput | U | Internal energy of the component [J] |
| output RealOutput | m | Mass of the component [kg] |
| output RealOutput | mXi[Medium.nXi] | Species mass of the component [kg] |
| output RealOutput | mC[Medium.nC] | Trace substance mass of the component [kg] |
| input RealInput | C_flow[Medium.nC] | Trace substance mass flow rate added to the medium |